Capti ReadBasix Tests
ReadBasix assesses 5 foundational reading skills and basic reading comprehension. Each skill can be assessed together or individually; the entire battery of 6 subtests takes students 45-60 minutes on average and up to 84 minutes if timed. The assessment time can be reduced by focusing on specific skills, most of which can be assessed in 5-10 minutes each. Each subtest has 3 levels of difficulty that are automatically personalized to students' levels based on the results of the previous administration of the ReadBasix diagnostic assessment or the ReadRoutix screener.

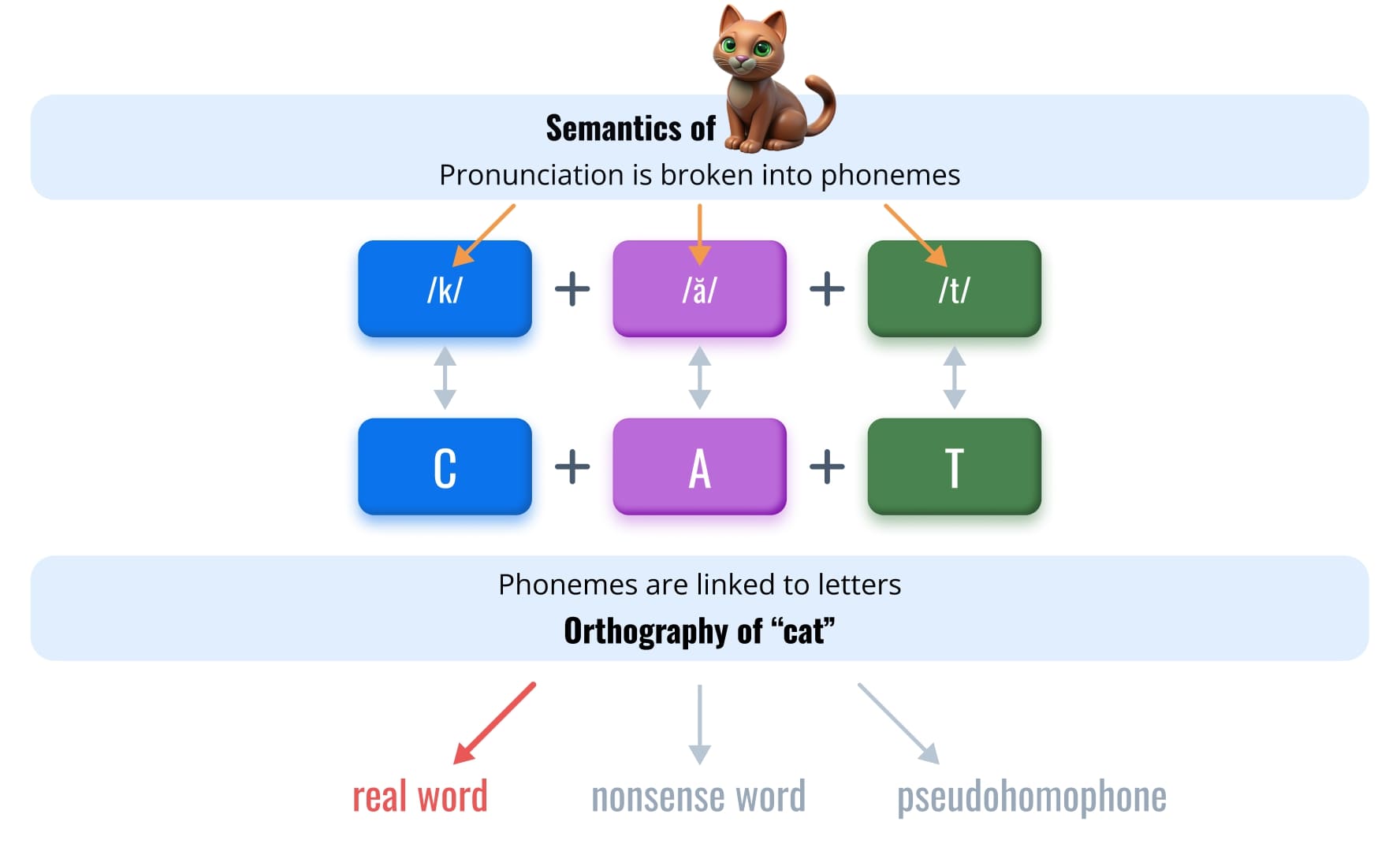
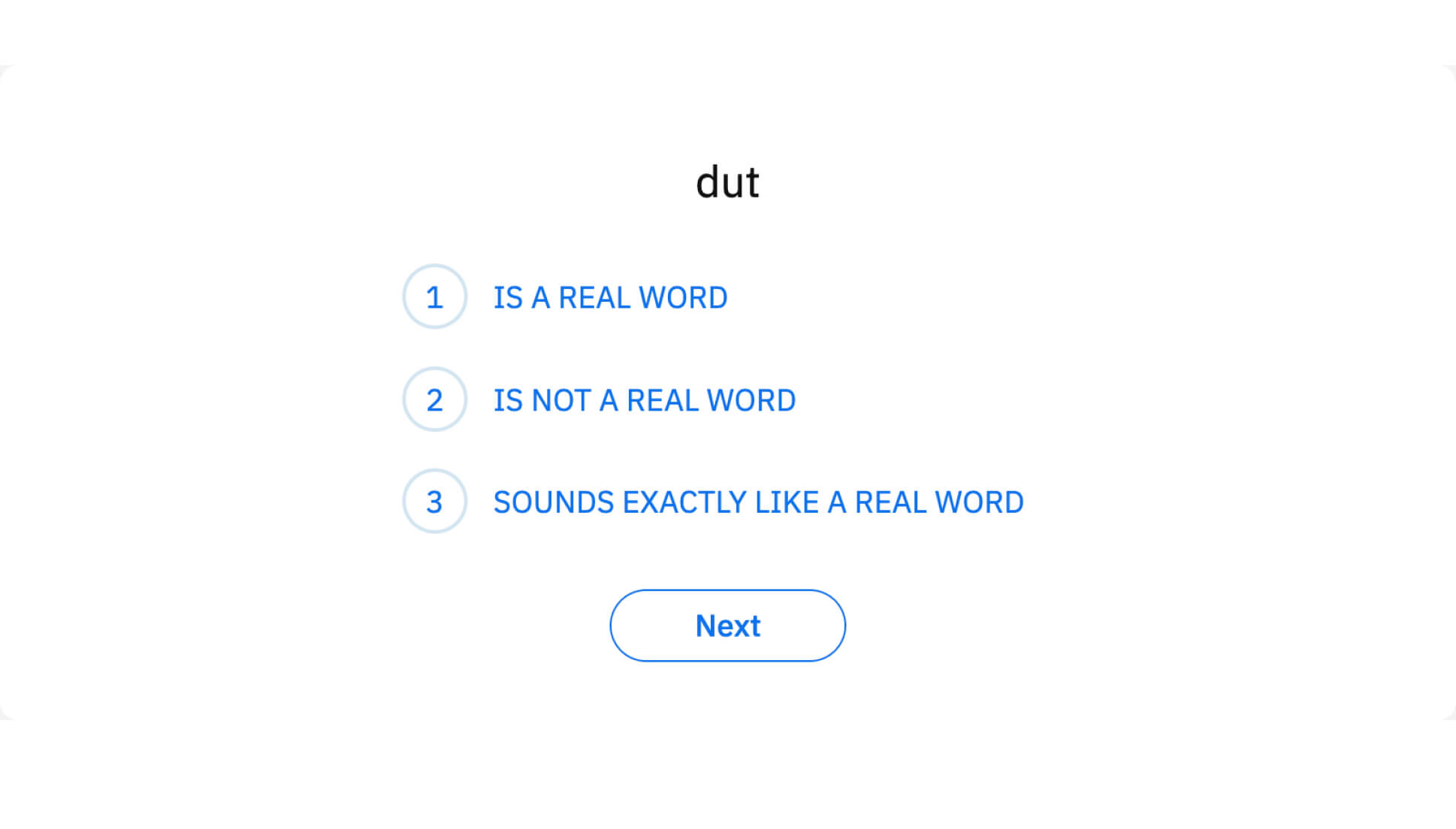
Word Recognition and Decoding
Sight word recognition concerns the ability to accurately and efficiently recognize known words in printed text. Phonological decoding is the process of linking letters with their sounds to read new words. Both are needed to support vocabulary acquisition and fluent reading. Low accuracy or low automaticity of decoding is the primary symptom of a reading disability or dyslexia.
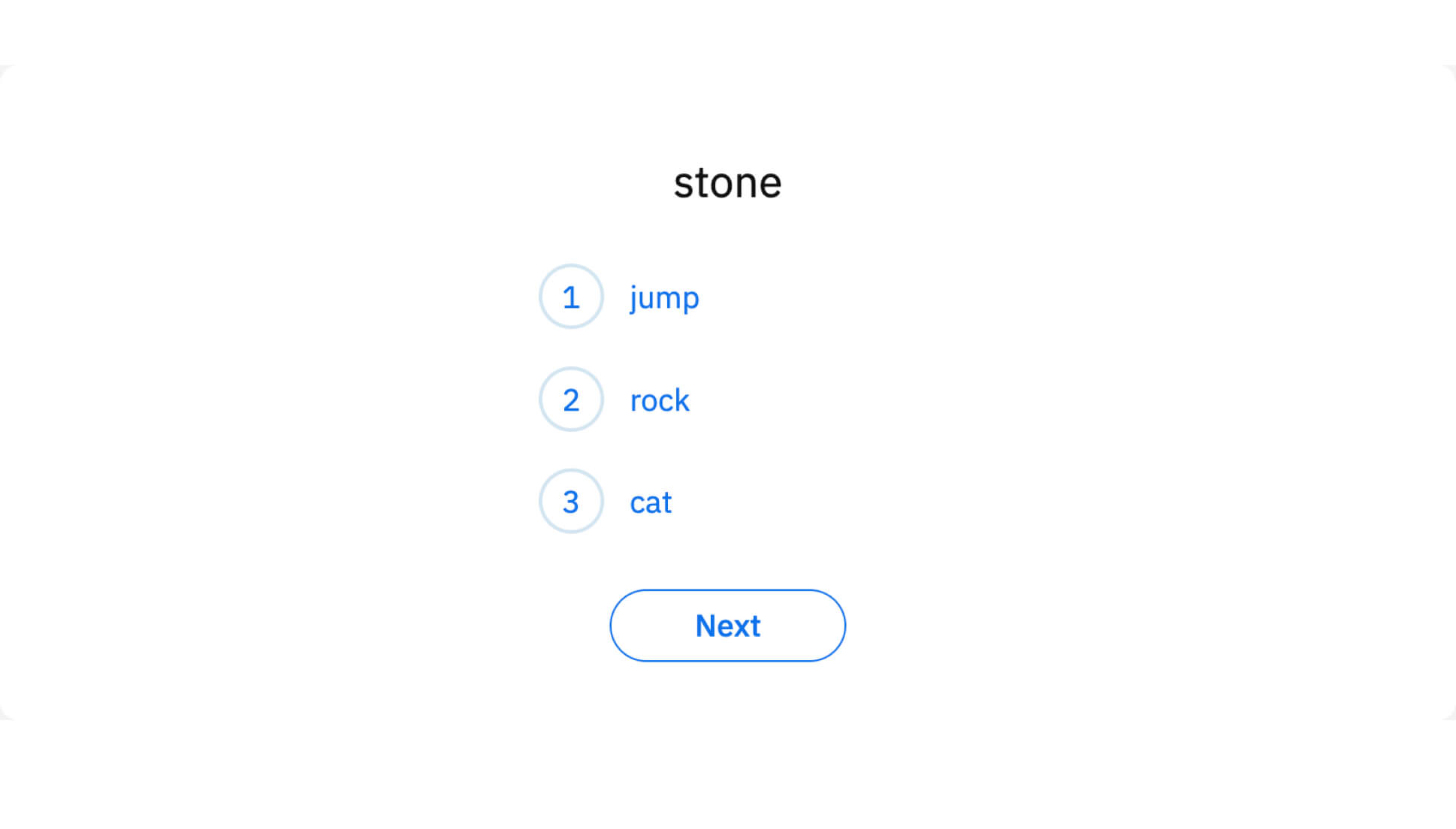
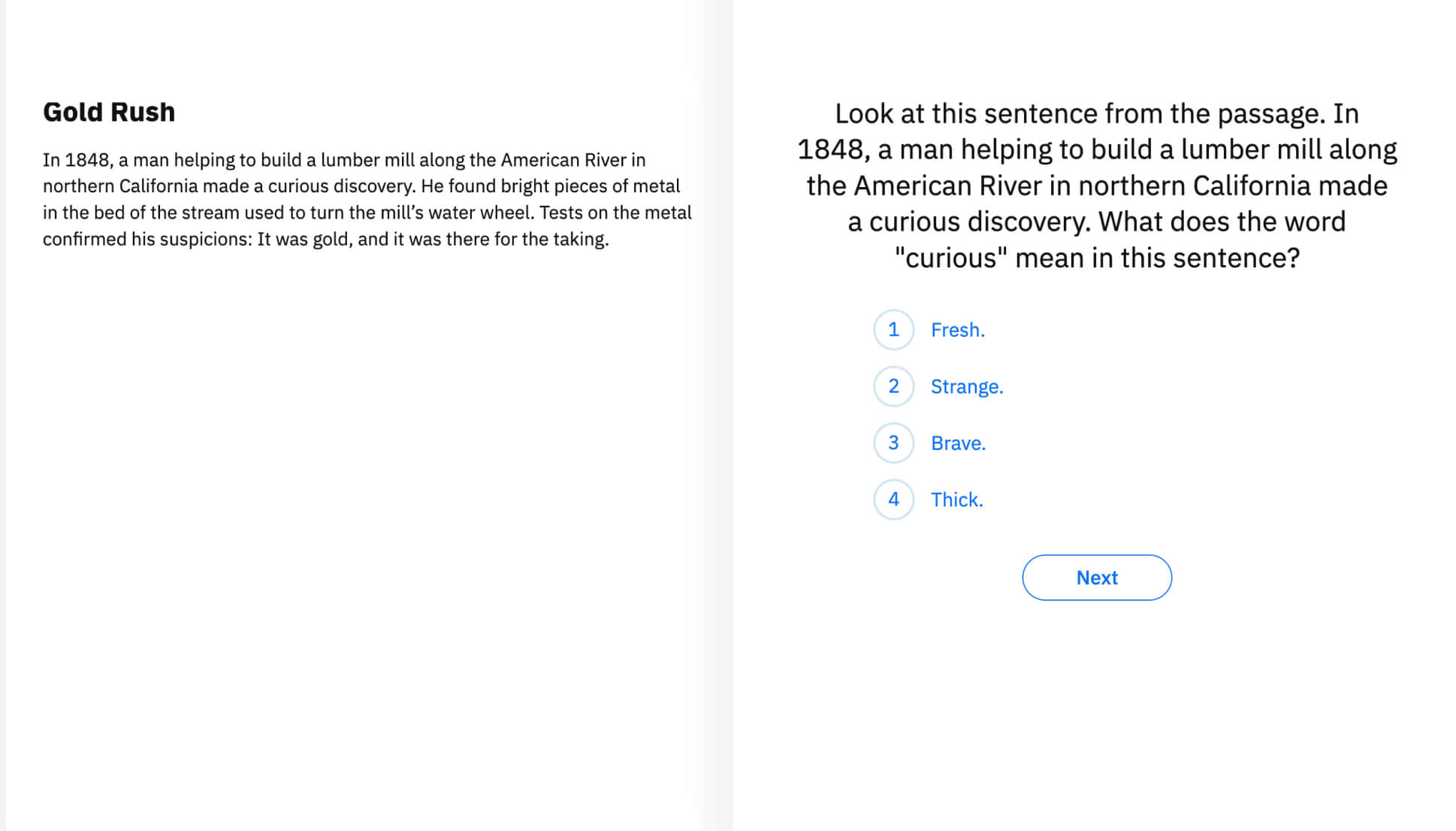
Vocabulary
Vocabulary knowledge helps derive the meaning of words and their associations to related words ("forest" to "trees"). Some estimates indicate that successful reading comprehension requires knowing the meaning of 95-98 percent of the words in text; thus, students with poor knowledge of grade-level vocabulary will struggle to understand disciplinary content.
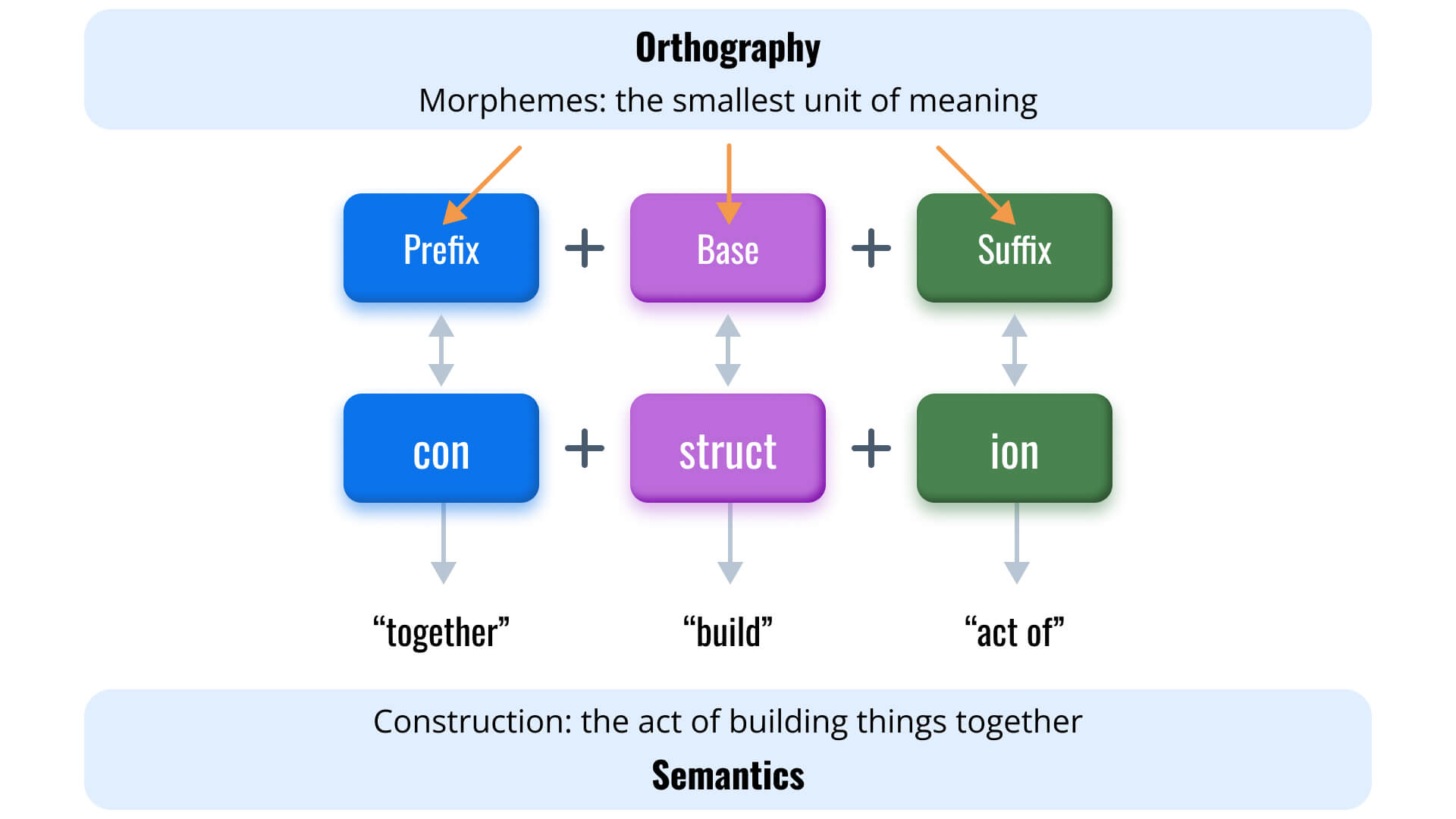
Morphology
Morphological awareness is the ability to identify and use various word parts. The subtest measures derivational morphology—those words that have prefixes and suffixes attached to a root to recognize words, comprehend sentences, and learn the meaning of new words. Morphology is important for developing new vocabulary and differentiating nuances in a word's meaning. Below grade-level performance could indicate poor vocabulary knowledge and/or a lack of understanding of how words are constructed.
Sentence Processing
Skilled Sentence Processing is the ability to comprehend sentences of varying complexity using cues, such as temporal (before, second), referential (him, her, this, that), relational (less than, larger than), and causal (because, therefore) connectors and conjunctions. The ability to understand the nuanced meaning of sentences is important for grasping the overall meaning of text. Lower sentence processing skill can be due to weaknesses in the preceding skills and/or a lack of familiarity with cues.
Reading Efficiency
Reading Efficiency concerns the ability to silently read text accurately and at an appropriate rate for understanding. Below grade performance in fluency indicates weaknesses in one or more of the preceding foundational skills and/or a lack of stamina for sustained silent reading.
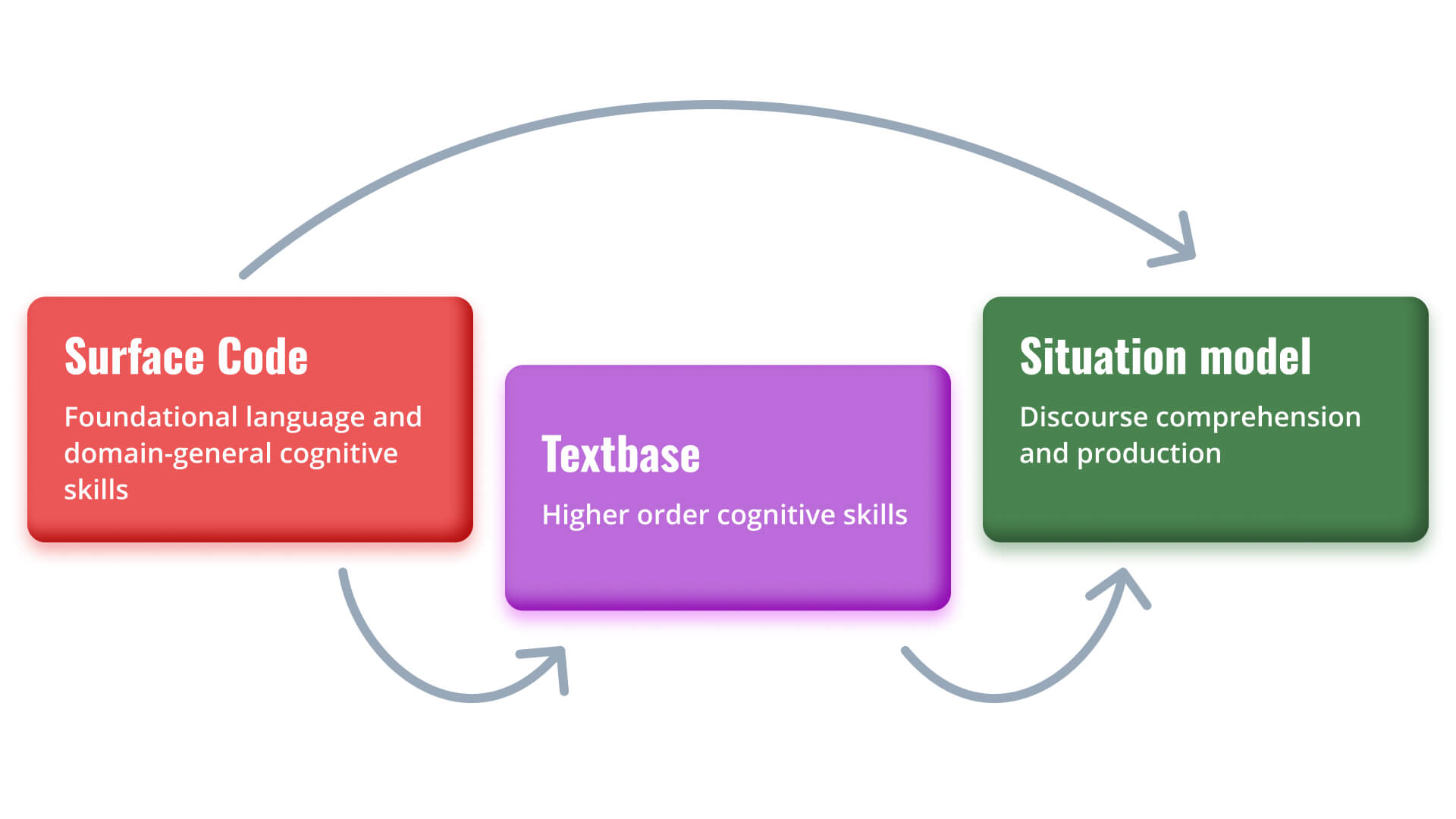
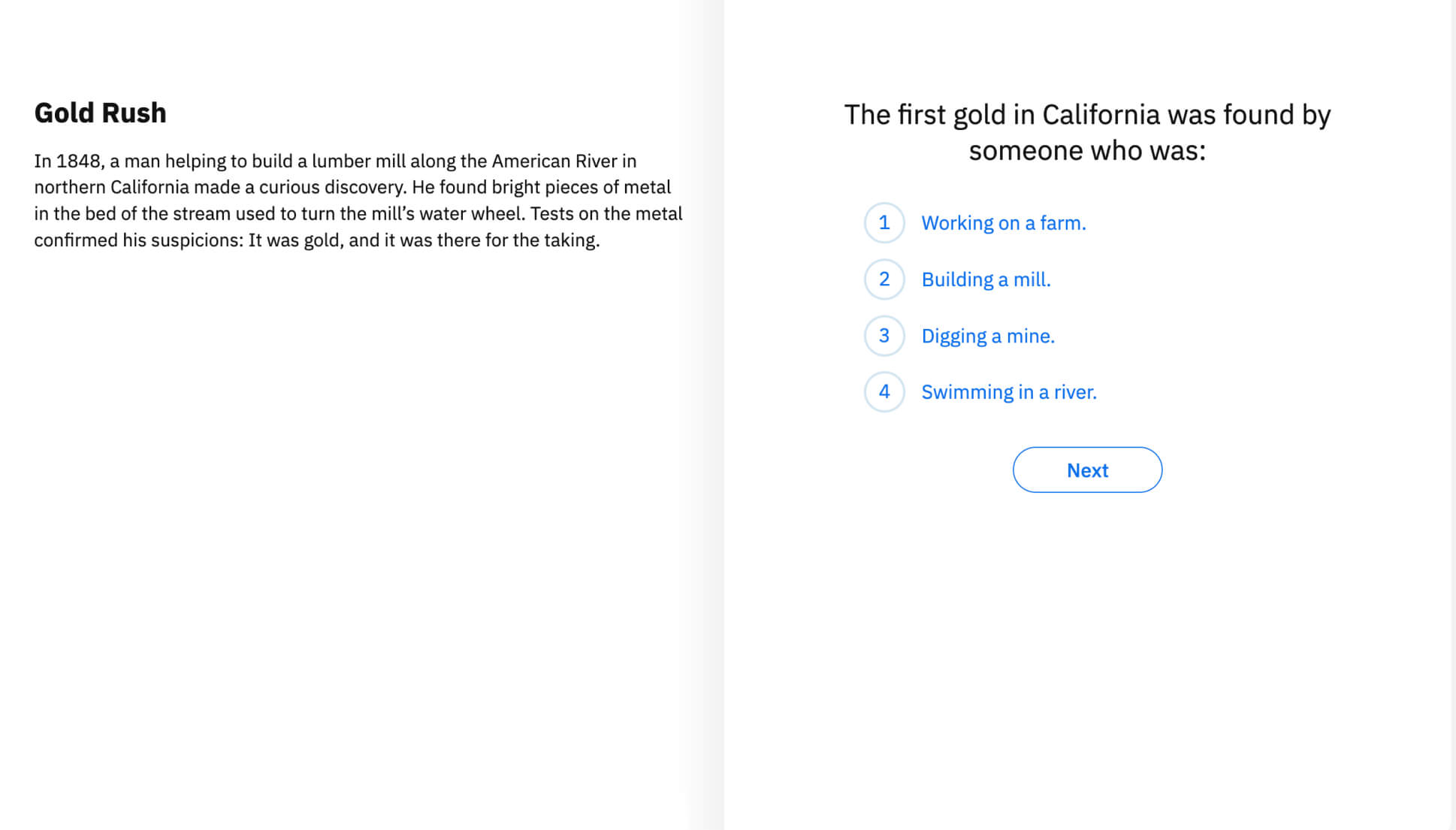
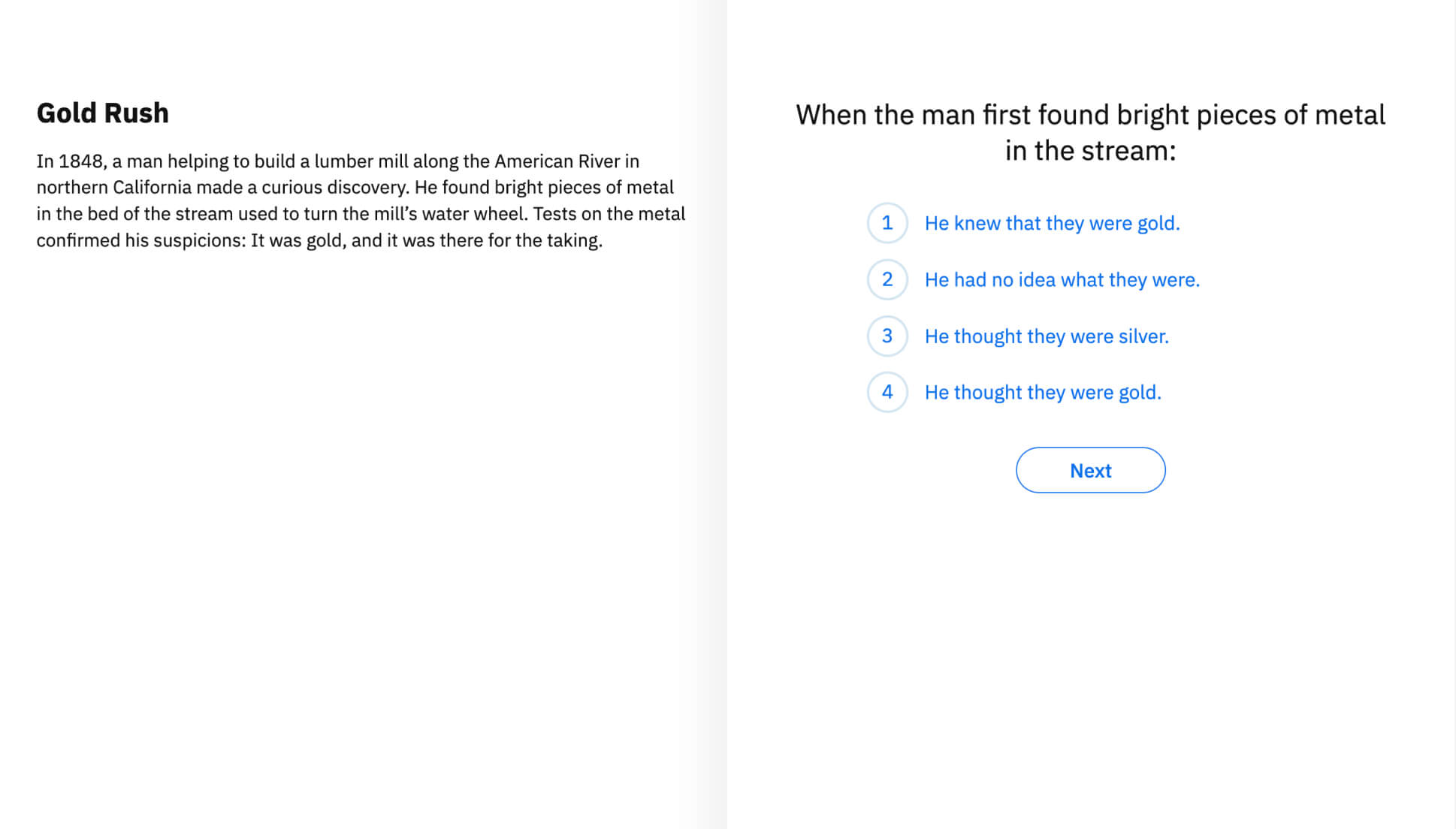
Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension is the ability to understand text by building an accurate mental model. This skill includes understanding the literal meaning, as well as making cross sentence or passage inferences. Below grade level performance indicates that the student is lacking in one or more foundational reading skills. Since reading comprehension is the overall goal of reading, it is imperative for any diagnostic reading assessment to include an overall comprehension measure.